PCB Assembly: The Foundation of Modern Electronics
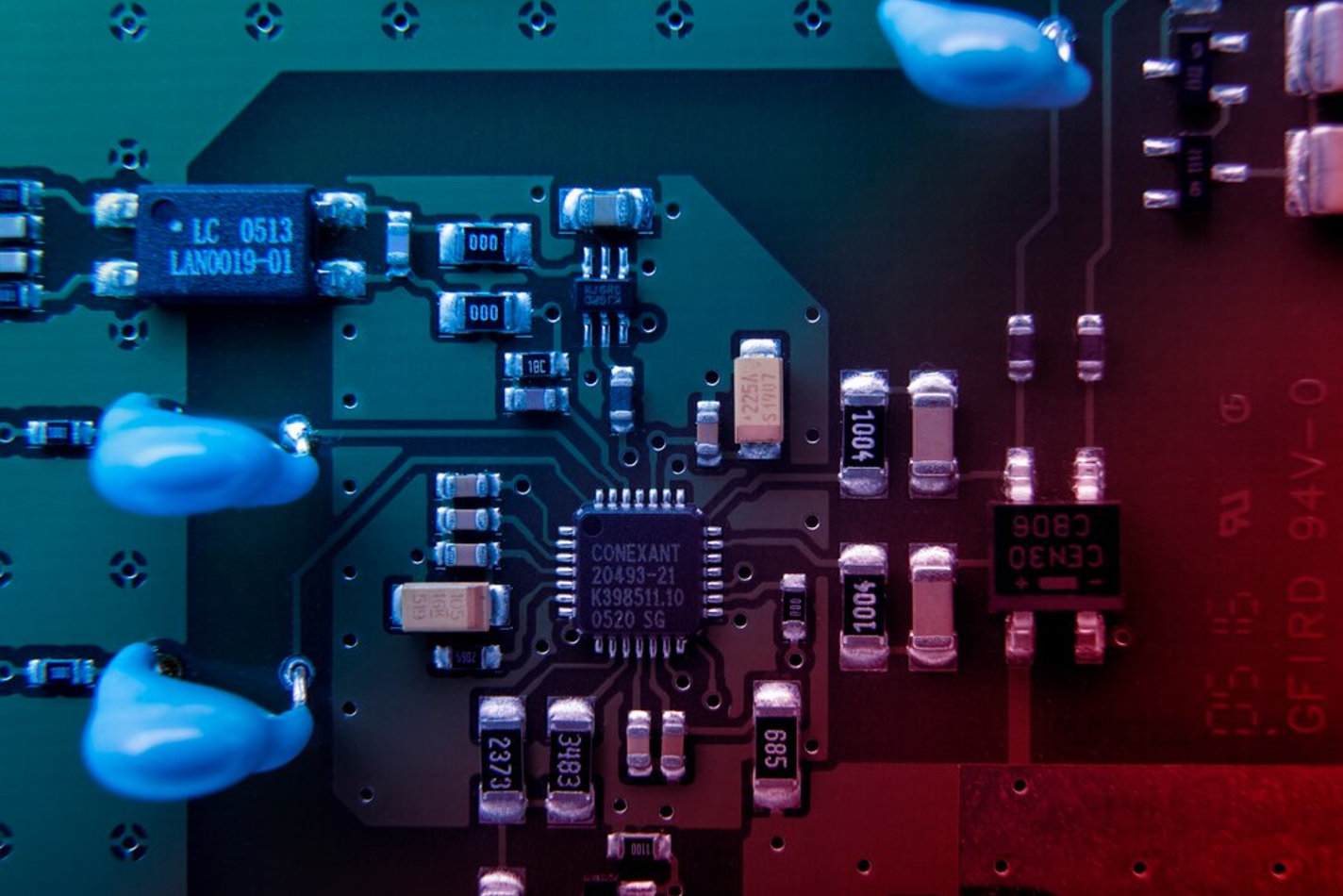
In the far-flung expanse of contemporary electronics, every appliance that we own is made possible by the uncelebrated victor called the Printed Circuit Board (PCB). Printed circuit boards (PCBs) serve as the foundation for our digital globe from mobile phones to health devices, automobile electronics and machines used in industries. How does an uncomplicated thought jotted down on paper change into a physical circuit that operates? This is what precisely takes place during the PCB assembling process.
To make the connection between design and real-life PCB assembly is something that encompasses more than just assembling components. The procedure turns abstract diagrams into functional electronics. But how far-reaching is this process? And what are the consequences of not getting it correct?
Understanding PCB Assembly: The Basics
The most important thing about this process is that it has to do with putting electrical parts on a board so they can work as a full circuit. Doing this makes sure that every part is positioned accurately and attached in such a way that the complete device works properly.
At a basic level, the production of printed circuit boards starts from an empty board, which serves as a blank canvas. The substrate used in most PCBs is a non-conductive material such as fibreglass and has some patterns etched on its surface that serve as electric paths – commonly made with copper. The traces thus formed interconnecting different components to allow electric signals to pass through them.
The addition of components transforms the entire process into a magical one. On the board, developers of computer programs or systems carefully position resistors, capacitors, microcontrollers and other electronic parts according to a preset mapping that corresponds with the design schematic. Herein lies an area where accuracy is critical – any minor misalignment could result in malfunctioning or breakdowns.
The Critical Steps of PCB Assembly
- Solder Paste Application: The first step in PCB assembly is making use of solder paste in applying it to the board. Solder paste consists of tiny balls of solder mixed with flux applied to the sections on which components will be mounted. When using this toaster oven, solder paste acts as an adhesive that holds the components in position while it forms a firm electrical link when heat is applied to it.
- Component Placement: Afterward, more components are layered onto the board. In current PCB assembly, it can be done with the help of automated machines that can do so at a rate of thousands of components per hour. The solder paste holds them on one hand and surface tension helps in keeping them in their position until they are soldered.
- Soldering: When the components have been positioned, the whole board goes through a procedure referred to as reflow soldering in which it is heated. The heating process makes it possible for them to melt and attach themselves to PCB. For double-sided boards, this process may then be done on their flip sides too.
- Inspection and Testing: Once soldering has been completed, the assembled PCB goes through an inspection for any defects or problems during this process known as inspection and testing. These include visual inspections, automated optical inspections (AOI) and sometimes, X-ray inspections to confirm fully formed solder joints that are hidden beneath the surface. In addition, functional testing is done to confirm if the PCB is working as intended.
- Final Assembly and Packaging: In the course of the procedure, the last operation entails inserting key links, different enclosures or other closing piece components that are necessary. After that, the finished PDBA is set for assembly into the final merchandise.
Challenges in PCB Assembly
Yet although it may look very easy to pick and place the elements for a PCB board, this process is full of complexities; thus one needs to have expertise in this area and apply accurate methods. To begin with, as devices become smaller, they demand more compact electronic parts too which pose some significant difficulties regarding placement accuracy and soldering operations.
Furthermore, due to the intricate nature of contemporary electronic design, a printed circuit board PCB is often required to accommodate various components ranging from small passive devices to big integrated circuits ICs. For all these devices to function together smoothly then there must be careful design and execution as well as planning.
One more major difficulty in the world of technology is verifying quality assurance. The defectiveness of just one solder joint has the potential to render an entire circuit board useless, necessitating expensive revisions or even worse, total loss of profitability for the final output. Therefore it is mandatory that thorough testing and inspection take a foremost position during PCB assembly processes.
The Role of Automation in PCB Assembly
In the present high-advanced world, automation takes an imperative position in PCB assembling. Automated assembly lines supplied with pick-and-place machines, reflow ovens as well and inspection systems can manufacture huge amounts of PCBs maintaining uniformity in quality. As a matter of fact, automation does not only raise efficiency but also minimizes the possibilities of human mistakes by making sure that every single printed circuit board (PCB) is built strictly according to specifications
Nonetheless, notwithstanding the benefits of mechanization, human skill is still necessary. For instance, there is a need for professionals with the technical know-how to design printed circuit boards, program and maintain computers as well as other devices, and identify problems encountered during assembling. It is through the coming together of human expertise and automated precision that the PCB assembly process meets today’s elevated requirements in electronics manufacturing
Conclusion: The Impact of PCB Assembly on Innovation
Assembly of PCBs is not only a technical process but also an essential step in transforming ideas into reality. From the newest phone models to life-saving medical devices, every cutting-edge electronic gadget relies on the accurate and effective assembly of its respective printed circuit boards (PCBs). The significance of PCB assembly will continue to rise with technological advancements, leading to the creativity and production of increasingly complex electronic appliances.
The next time you reach for your smartphone, operate machinery or switch on a light, stop to consider how intricate and amazing is PCB assembly. Our contemporary society would be remarkably dissimilar without it.